In the vast landscape of modern manufacturing, injection moulding stands tall as a versatile and efficient process for crafting a myriad of plastic products. In this in-depth exploration, we unravel the fundamental principles, delve into the core components of injection moulding machines, and guide you through the step-by-step journey of transforming raw materials into intricate shapes.
I. Understanding the Essence of Injection Moulding
A. Core Principles
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a precisely crafted mould to produce a desired shape. This method, with its roots dating back to the 19th century, has evolved into a cornerstone of mass production, enabling the creation of products that range from simple household items to complex automotive components.
B. The Process Flow
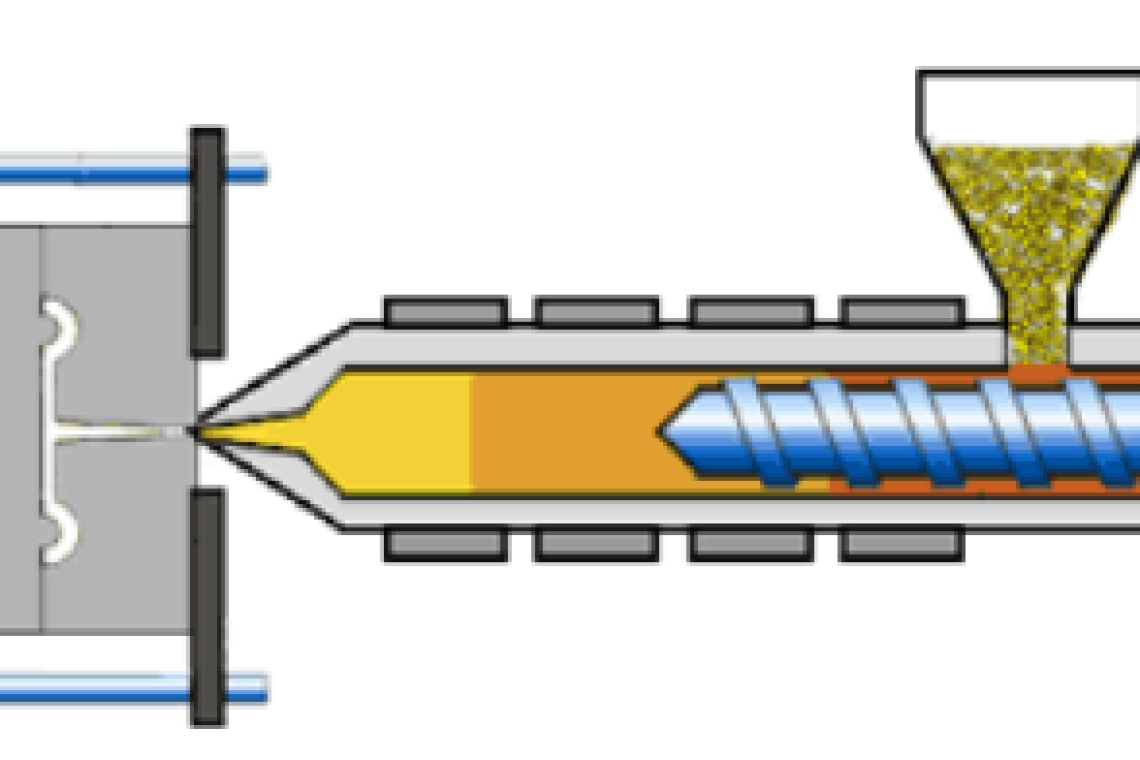
- Material Loading: The process commences with loading raw plastic material, usually in pellet or granule form, into the injection moulding machine.
- Melting and Injection: Within the injection unit, a rotating screw mechanism melts and homogenizes the material, which is then injected into the mould.
- Cooling and Solidification: As the molten material fills the mould, it cools and solidifies, taking the form of the mould cavity.
- Ejection: The final step involves ejecting the newly formed product from the mould, ready for further processing.
II. Dissecting the Injection Moulding Machine
To comprehend the intricacies of injection moulding, it’s imperative to understand the primary components of an injection moulding machine.
A. Injection Unit
- Feeding System: Raw plastic material is fed into a heated barrel through a hopper.
- Plasticizing and Injection: A rotating screw within the barrel plasticizes the material, and the resultant molten plastic is injected into the mould.
B. Mould
- Cavity and Core: The mould comprises two halves—the cavity and the core—that, when closed, create the desired shape.
- Cooling System: Precision cooling is crucial to control the solidification process and ensure uniform material distribution.
C. Clamping Unit
- Secure Closure: The clamping unit applies sufficient force to keep the mould securely closed during injection.
- Structural Integrity: This unit plays a pivotal role in maintaining the structural integrity of the final product.
III. Mastering Material Selection
Material selection is a critical aspect that directly influences the properties, durability, and performance of the final product.
A. Thermoplastics
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing.
- Polypropylene (PP): Exhibits high stiffness, low friction, and is resistant to acids and bases.
- Polystyrene (PS): Offers clarity, low cost, and is widely used in disposable consumer goods.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Known for its chemical resistance, durability, and versatility.
B. Thermosetting Plastics
- Phenolic Resins: Possesses excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability.
- Melamine: Recognized for its hardness, scratch resistance, and electrical insulating properties.
IV. Navigating Challenges in Injection Moulding
A. Common Challenges
- Warping and Shrinkage: Addressing issues related to material shrinkage and warping during cooling.
- Tooling Costs: The high initial costs associated with mould production.
B. Innovative Solutions
- 3D-Printed Tooling: Utilizing 3D printing for rapid prototyping and tooling, reducing lead times and costs.
- Sustainable Materials: The integration of eco-friendly materials and sustainable practices in injection moulding.
V. Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to the basics of injection moulding, it’s evident that this manufacturing process is a symphony of technical prowess, engineering innovation, and material science. Whether you’re a novice exploring the world of manufacturing or an industry professional seeking to deepen your understanding, injection moulding remains a fascinating and integral part of the production landscape. Stay tuned for our next installment, where we delve into the intricate world of material selection in injection moulding.