Product Certification: Ensuring Quality and Compliance
So What is Product Certification?
Product Certification: Product certification is an essential process for manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with established quality and safety standards. It’s a critical, often mandatory, step for products entering various markets, especially those with potential safety implications for consumers and the environment. Certification acts as a seal of approval from regulatory bodies or industry standards organizations, confirming that a product has met specific criteria. These criteria can range from performance characteristics to longevity, environmental impact, and, most importantly, safety. This introduction delves into the complex web of certification processes, highlighting their pivotal role in market access and consumer trust, while also considering the challenges manufacturers face in achieving and maintaining these standards.
Quality Control vs. Product Certification
The differences:
Product certification and quality control are two distinct aspects of product management and assurance, each serving a unique role in a product’s lifecycle. Quality control is an internal process, primarily focused on ensuring that products meet specific quality standards and criteria set by the manufacturer. It involves a series of checks, tests, and inspections conducted throughout production to identify and correct defects or deviations from the desired quality. Quality control is a proactive, ongoing activity to maintain consistent product quality and prevent errors before they reach the consumer.
In contrast, product certification is an external validation process conducted by an independent third party, or internally using third-party international recognised standards. It verifies that a product meets predefined standards set by an external regulatory body or standards organization. Product certification is typically a more formal, structured process that involves rigorous testing and evaluation of a product against specific industry or safety standards. The objective of product certification is to assure consumers, regulators, and other stakeholders that the product adheres to the required standards and is safe and suitable for its intended use. While quality control is an internal, continuous process focusing on quality maintenance, product certification is an external, often periodic process aimed at formal compliance and recognition.
In essence, quality control is about maintaining standards within the company, whereas product certification is about proving compliance with external standards to the world.
The Certification Process: The certification process involves several stages:
Stage 1: Standard Identification: This stage involves identifying the specific standards and regulations that apply to the product. These standards vary significantly depending on the product’s intended use and the markets where it will be sold. For instance, electronic products sold in the European Union must comply with CE standards, the UK the UKCA standards, while those in the United States might need to meet FCC guidelines.
- Understanding Product Scope: Before identifying the relevant standards, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the product’s features, uses, and potential risks. This understanding helps in accurately determining which standards apply.
So why is this important?: Different products are subject to different regulations and standards based on their type, usage, and the risks they pose. A thorough understanding of the product’s scope ensures that the correct standards are identified. For instance, a wireless computer mouse and a wired one might fall under different subsets of standards due to their different operating mechanisms.
Knowing the product’s features and potential risks is essential to ensure that it meets safety requirements. This is crucial not only for legal compliance but also for protecting the end-user. For example, understanding that a product will be used by children could necessitate stricter safety standards.
Understanding the product scope from the outset can streamline the certification process. It helps in avoiding unnecessary testing and reduces the risk of non-compliance, which can be costly and time-consuming to rectify later.
Knowing the product inside out helps in identifying and mitigating potential risks, be they related to user safety, environmental impact, or operational efficiency. This proactive approach in addressing risks is essential for a product’s long-term success and reputation in the market.
But remember….. understanding the product scope is not just about ticking boxes for compliance; it’s about ensuring product safety, market suitability, legal conformity, and overall quality, all of which are crucial for the product’s success and the manufacturer’s reputation.
- Market-Specific Requirements: Each target market has its own set of standards and regulations. For example, electronic products must comply with different standards depending on their intended market: CE standards in the European Union, UKCA standards in the United Kingdom, and FCC guidelines in the United States.
Understanding and adhering to market-specific requirements is crucial in the product certification process for several key reasons:
Each geographical market has its own legal framework and set of standards. Compliance with these standards is often legally required to sell a product in that market. For example, electronic products must meet CE standards in the European Union, UKCA standards in the United Kingdom, and FCC guidelines in the United States. Failure to comply can lead to legal repercussions, including fines, product recalls, or bans.
Market-specific standards are often designed to ensure product safety and reliability. By complying with these standards, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to consumer safety, which helps in building consumer trust and brand credibility.
Compliance with local regulations is a prerequisite for market access. Understanding and meeting these requirements is essential for entering and expanding in different markets. It allows manufacturers to avoid barriers to entry such as customs rejections or legal challenges.
Market-specific standards often push manufacturers to meet higher quality and performance benchmarks. This can lead to product improvements, innovation, and higher customer satisfaction, giving a competitive edge in the market.
Non-compliance can result in risks such as product recalls, legal action, and damage to brand reputation. Understanding and adhering to market-specific requirements mitigate these risks.
Different markets may have unique cultural or environmental considerations that are reflected in their standards. Compliance ensures that products are suitably tailored for the local environment and consumer preferences.
Understanding market-specific requirements early in the product development process can save time and resources. It prevents the need for costly redesigns or modifications later in the process.
Again, remember… Understanding and meeting market-specific requirements is not just about legal compliance; it’s about ensuring product relevance, safety, and quality in different markets, which ultimately contributes to a company’s global success and sustainability.
An Example of CE markings being applied incorrectly from the RAPEX alert system:
The RAPEX alert case for the toy car named “Feed – tank” resulted in a product recall due to a choking hazard.
The plastic toy car, which comes in various colours and features a painted face, four wheels with an inertial mechanism, and a mobile tank with a clear plastic cover, was found to have small parts.
These small parts pose a choking risk to children who might put them in their mouths.
Consequently, the product does not comply with the Toy Safety Directive and the European standard EN 71-1. As a measure to protect consumer safety, the product was ordered to be withdrawn from the market.
The RAPEX (Rapid Alert System for Non-Food Products) is an important tool used by the European Union to ensure consumer protection across its member states. This system facilitates rapid information exchange among EU member countries and the European Commission about dangerous non-food products posing risks to health and safety of consumers.
When a product, ranging from toys to electrical appliances, is identified as dangerous, the details are circulated through RAPEX. This alert includes information on the nature of the risk, the measures taken to address it (such as withdrawal from the market or recall from consumers), and the product’s identification details. RAPEX thus plays a crucial role in preventing or restricting the sale of hazardous products, ensuring swift and coordinated responses across Europe to protect consumer safety.
Find more here: RAPEX ALERTS

- Regulatory Landscape Analysis: This step involves keeping up-to-date with the latest regulatory changes in each market. Regulatory requirements can frequently change, and compliance is dependent on adhering to the most current standards.
Regulatory Landscape Analysis is a crucial step in the product certification process, particularly for maintaining compliance with international standards. Its importance can be outlined as follows:
Ensuring Continued Compliance: Regulatory standards are not static; they evolve over time. Changes may be due to technological advancements, new safety findings, or shifts in public policy. Staying informed about these changes is essential to ensure that a product remains compliant over its lifecycle.
Market Access and Competitiveness: Markets often update their regulations to reflect new safety, environmental, or quality standards. By keeping up-to-date with these changes, companies can ensure uninterrupted access to these markets. It also helps them maintain a competitive edge, as products adhering to the latest standards are often viewed as safer, higher quality, or more environmentally friendly.
Risk Management: As discussed above failure to comply with current regulations can lead to various risks, including fines, product recalls, and reputational damage. Regular regulatory landscape analysis helps in identifying and mitigating these risks proactively.
Strategic Planning and Innovation: Understanding upcoming regulatory trends can inform strategic business decisions and product development. Companies can innovate and adapt their products to meet future standards, positioning themselves as market leaders.
Global Standardization: For companies operating in multiple markets, keeping track of regulatory changes helps in harmonizing product designs to meet diverse international standards, simplifying production and reducing costs.
Consumer Safety and Trust: Adherence to the latest regulations demonstrates a commitment to consumer safety and environmental responsibility, which can enhance brand reputation and consumer trust.
Regular analysis of the regulatory landscape is vital for ensuring ongoing compliance, managing risks, maintaining market access, supporting strategic decision-making, and upholding consumer safety and trust.
Where can I find the latest Product Standards in the UK?
To find the latest standards update list for the UK, you can visit the websites of several key organizations responsible for standards and regulations in the UK. Here are some sources where you can access this information.
British Standards Institution (BSI): The BSI is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. They publish and update British Standards, and their website provides access to the latest standards, including those relevant to product certification. Visit their website at bsigroup.com.
Trading Standards: Trading Standards is responsible for enforcing legislation that protects consumers and supports fair and safe trading. Their website and local offices can provide information on current product safety standards and regulations. Visit tradingstandards.uk.
UK Accreditation Service (UKAS): UKAS is the national accreditation body, tasked with assessing the competence and integrity of organizations offering testing, inspection, calibration, certification, and verification services. Visit ukas.com for information on accredited services and standards.
Office for Product Safety & Standards (OPSS): Part of the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy, OPSS provides guidance on product safety regulations in the UK. Visit their section on the UK Government website for more information.
It’s also a good practice to subscribe to newsletters or alerts from these organizations to receive regular updates on standards and regulatory changes in the UK.
- Consulting with Experts: Often, manufacturers consult with regulatory experts or legal advisors to ensure that they correctly identify and interpret the applicable standards. This is especially important for complex products or when entering new markets.
Need Expert Guidance for Your Product Testing and Compliance? Contact MerchSprout Today!
Navigating the complexities of product standards and regulations can be a daunting task, especially for intricate products or when exploring new markets. At MerchSprout, we understand the critical importance of getting it right. That’s why we’re here to offer you the expertise and support you need.
Why Choose MerchSprout?
Tailored Expertise: Our team of regulatory experts and legal advisors specializes in accurately identifying and interpreting applicable standards for a wide range of products. Whether you’re dealing with high-tech electronics, innovative toys, or any other product, we have the know-how to guide you.
Market-Specific Insights: Entering new markets? We’re adept at navigating various international compliance landscapes. Our insights can help you avoid costly missteps and ensure smooth market entry.
Comprehensive Testing Solutions: At MerchSprout, we don’t just advise – we facilitate. We connect you with top-tier testing facilities to ensure your product not only meets but exceeds the required standards.
Risk Mitigation: With our guidance, reduce the risk of non-compliance, such as fines, recalls, or reputation damage. We focus on compliance so you can focus on innovation and growth.
Trusted by Industry Leaders: Leading manufacturers trust MerchSprout for our reliable, informed, and efficient approach to product testing and compliance.
Ready to Ensure Your Product's Compliance with Confidence?
Stage 2: Comprehensive Product Testing: After identifying the relevant standards, the product undergoes rigorous testing. These tests are often conducted in specialized laboratories equipped to simulate various conditions and use-cases to ensure the product’s compliance with standards. This step is vital in determining whether the product is safe for use, meets performance expectations, and adheres to any environmental regulations.
- Selection of Testing Laboratories: The testing is usually conducted in specialized laboratories that are accredited to perform such assessments. These laboratories have the necessary equipment, expertise, and authorization to conduct tests as per the relevant standards. It’s essential to choose a lab that can test according to the specific standards your product needs to meet.
Selecting the right testing laboratory is a crucial step in the product certification process, especially for manufacturers and importers dealing with Chinese test labs. Here’s why this stage is so important and needs careful consideration:
1. Accuracy and Reliability of Test Results: Specialized testing laboratories are equipped with the necessary technology and expertise to accurately assess a product’s compliance with specific standards. The reliability of these test results is paramount, as they form the basis for certifying that the product is safe and meets regulatory requirements. Choosing a test lab is a lot like choosing the correct supplier, conducting due diligence is a must. Sites like the UKCA have a test lab accreditation checker. Ensure that you have checked that the test lab is accredited for the test standards they are testing to.
2. Accreditation and Authorization: Accredited laboratories have been evaluated and recognized by authoritative bodies for their competency in conducting specific tests. This accreditation ensures that the tests are performed to the highest standards and are in line with international or regional regulatory requirements.
UK Accreditation Service (UKAS): UKAS is the national accreditation body, tasked with assessing the competence and integrity of organizations offering testing, inspection, calibration, certification, and verification services. Visit ukas.com for information on accredited services and standards.
3. Understanding of Specific Standards: Different products are subject to different standards based on their type, use, and target market. Laboratories with experience in specific standards can provide more precise and relevant testing services. For example, a laboratory specializing in electronic devices will be better equipped to test for EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) and safety standards applicable to these products. If in doubt, ask for accreditation, then use online checkers to ensure the test labs are using an in date correctly issued certificate.
4. Adherence to Market-Specific Regulations: Especially in the context of global trade, products may need to comply with standards that vary from one region to another. A laboratory familiar with these variations can ensure that the product meets all target market requirements, whether for the EU, the US, or other regions.
5. Challenges with Chinese Test Labs: When working with Chinese test labs, the onus often falls on the manufacturer or importer to know which standards their products need to comply with. This can be particularly challenging given the breadth and complexity of standards across different markets. A lack of understanding can lead to incorrect or incomplete testing, which in turn can result in non-compliance, product recalls, or legal issues.
6. Cost and Time Efficiency: Choosing the right laboratory can also be cost-effective. Labs that are well-versed in specific standards can conduct tests more efficiently, reducing the turnaround time and potentially the cost of testing.
7. Risk Mitigation: Accurate testing and compliance reduce the risk of product recalls, legal penalties, and damage to brand reputation. It’s essential for ensuring the safety and satisfaction of the end-users, which is ultimately beneficial for the long-term success of the product.
Selecting the right testing laboratory, especially when dealing with Chinese test labs, is not just a procedural step but a strategic decision. It requires a clear understanding of the applicable standards, the specific needs of the product, and the regulatory environment of the target market. This decision can have significant implications for the product’s market viability, legal compliance, and overall brand integrity. Manufacturers and importers must approach this step with diligence and informed decision-making to ensure successful product compliance.
Ready to Ensure Your Product's Compliance with Confidence?
- Testing Scope and Methodology: The scope of the testing depends on the product type, its intended use, and the identified standards. For example, electronic products may require electromagnetic compatibility testing, safety testing, and performance evaluations. The testing methodologies are defined in the standards and are designed to comprehensively assess the product’s compliance.
The Importance of Tailored Testing Scope The scope of testing is a critical aspect of product certification, as it ensures that each product is evaluated against relevant and specific criteria. This tailored approach is crucial because different products, due to their varied types and uses, pose different kinds and levels of risk to users and the environment.
For instance, electronic products, which are an integral part of daily life and often operate in close proximity to other electronic devices, must undergo electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing. This ensures that they neither emit harmful electromagnetic interference nor are unduly affected by it.
Similarly, safety testing is paramount for products that could pose a physical risk to users, such as electrical appliances, to prevent accidents like fires or electric shocks. Performance evaluations are also essential to ensure that products meet functional expectations and do not fail prematurely, which can have significant implications for both consumer satisfaction and brand reputation.
By defining a testing scope that aligns with the product type and its intended use, manufacturers can address the specific risks associated with their products, ensuring that they are safe, reliable, and fit for purpose.
Defined Methodologies in Testing The methodologies used in product testing are meticulously defined within the relevant standards to provide a consistent, reliable, and objective assessment of a product’s compliance.
These methodologies are developed by experts and are based on scientific principles and real-world scenarios. They ensure that testing is comprehensive and leaves no room for ambiguity in the assessment of a product’s safety and performance. For example, the methodology for EMC testing involves specific procedures to measure the electromagnetic emissions of a product and its susceptibility to external electromagnetic interference.
This precision is crucial in providing accurate and repeatable results, which are essential for fair and consistent product evaluation across different manufacturers and product batches.
The defined methodologies also facilitate international trade by ensuring that products tested in different countries or by different laboratories can be compared on an equal footing, fostering trust among consumers, regulators, and trading partners.
Comprehensive Assessment for Compliance Assurance The overarching goal of employing specific testing scopes and methodologies is to comprehensively assess a product’s compliance with the identified standards.
This comprehensive assessment is vital not only for adhering to legal requirements but also for ensuring the product’s overall quality and safety. When products are tested thoroughly, potential defects or non-compliances can be identified and rectified before the products reach the consumer.
This proactive approach to quality assurance helps in avoiding costly recalls, legal liabilities, and damage to the brand’s reputation. Furthermore, in markets where consumer awareness and expectations are high, such rigorous testing and compliance to standards are often a key differentiator for products, influencing purchasing decisions and consumer trust.
Ultimately, the detailed scope and methodology of testing underscore a commitment to consumer safety, product reliability, and adherence to ethical and legal standards, which are fundamental to the success and sustainability of any product in the market.
- Simulating Conditions and Use-Cases: The product is subjected to various conditions and scenarios that simulate its real-world usage. This can include stress tests, durability tests, environmental impact assessments, and user safety evaluations. For instance, a smartphone might be tested for its ability to withstand drops, its battery life, and its emissions.
The Foundation of Correct Test Standard Selection The efficacy of product testing hinges fundamentally on selecting the appropriate test standards. It’s a foundational step that dictates the relevance and effectiveness of all subsequent tests.
Standards are developed by experts and are tailored to specific product types, addressing the unique risks and requirements associated with each. For instance, the standards selected for testing an electronic device like a smartphone will focus on aspects such as electromagnetic compatibility, battery safety, and screen durability.
It’s crucial to remember that tests are only as effective as the standards they aim to validate. Choosing the right standards ensures that the testing process is not just a routine procedure, but a meaningful assessment that genuinely verifies a product’s safety, functionality, and compliance.
Simulating Real-World Conditions and Use-Cases Once the correct standards are selected, the next vital step is simulating real-world conditions and use-cases.
This approach tests how the product will perform under various scenarios it is likely to encounter during its lifecycle. For example, a smartphone may undergo drop tests to assess its durability or battery life tests to ensure longevity.
These simulations are crucial in bridging the gap between laboratory conditions and the actual user environment, providing a realistic assessment of the product’s resilience, reliability, and safety.
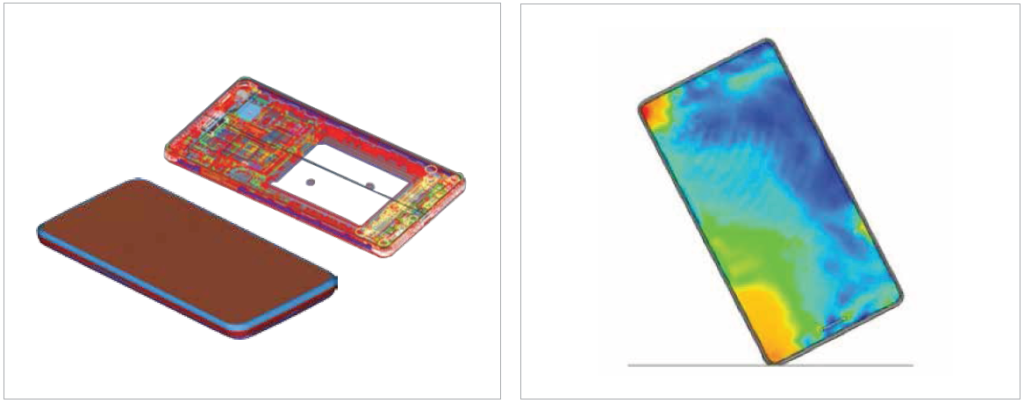
Stress and Durability Testing for Longevity Stress and durability testing further build on the foundation of correct standard selection. These tests subject the product to extreme conditions to evaluate its robustness and endurance.
For example, home appliances might be tested for their ability to function effectively over thousands of operating cycles. This phase is integral in identifying design flaws or material weaknesses, ultimately leading to products that are more durable and reliable, which enhances consumer trust and satisfaction.

Environmental and User Safety Assessments Environmental impact assessments and user safety evaluations are the final layers in this comprehensive testing process. They ensure the product’s compliance with environmental standards and assess its safety for users. These assessments are vital in today’s market, where regulatory compliance, sustainability, and consumer safety are paramount.
They involve evaluating a product’s ecological footprint, such as energy consumption or emissions, and ensuring it poses no harm to users, like checking toys for choking hazards. These evaluations are not just regulatory formalities but are essential in safeguarding consumer welfare and the environment, thereby upholding the product’s integrity and the brand’s reputation.
This stage of product testing is a crucial step that bridges the gap between controlled lab environments and the unpredictable nature of real-world usage.

By subjecting products to stress tests, durability evaluations, environmental impact assessments, and user safety checks, manufacturers can gain a comprehensive understanding of how their products will perform under actual conditions.
Whether it’s a smartphone enduring drop tests and battery longevity checks or a toy undergoing safety evaluations, each test plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the final product is not just theoretically sound, but practically resilient and safe for consumers.
This process is integral to the lifecycle of product development, serving as a key determinant of a product’s market readiness and long-term success. It underlines the commitment of manufacturers to quality and safety, fortifying consumer trust and fulfilling regulatory obligations. Ultimately, the rigorous simulation of conditions and use-cases is fundamental in delivering products that meet the high standards expected by today’s consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
- Safety and Performance Assessments: These tests evaluate whether the product is safe for the end-user and whether it performs as expected. This is crucial for consumer protection and to ensure that the product does not pose any harm during normal operation.
Safety and Performance Assessments are pivotal in product testing. They ensure a product’s safety and functionality for end-users. This process is crucial for consumer protection. It also guarantees that the product poses no harm during normal operation.
The first step in safety assessments is identifying potential risks. These can range from electrical hazards to mechanical injuries. For each identified risk, specific tests are designed. For instance, electrical products undergo rigorous insulation and short-circuit tests.
These tests aim to verify compliance with established safety standards. Standards set by regulatory bodies dictate these safety benchmarks. The outcome of these tests is meticulously documented and analyzed. Any failure to meet safety standards leads to redesign or adjustments.

Performance assessments begin by defining expected performance criteria. These criteria are based on the product’s intended function. Functional testing then ensures the product performs as expected. This includes efficiency checks, response time testing, and operational assessments.
Durability is also a key focus in performance testing. Products are subjected to conditions simulating extended use. This determines long-term functionality and safety. The results of these tests are evaluated against the set performance criteria.
Products meeting or exceeding these criteria move closer to certification. Those that don’t require further improvement or redesign. In summary, Safety and Performance Assessments are essential. They uphold consumer safety and product reliability in the market.
Product Certifcation- A real world example
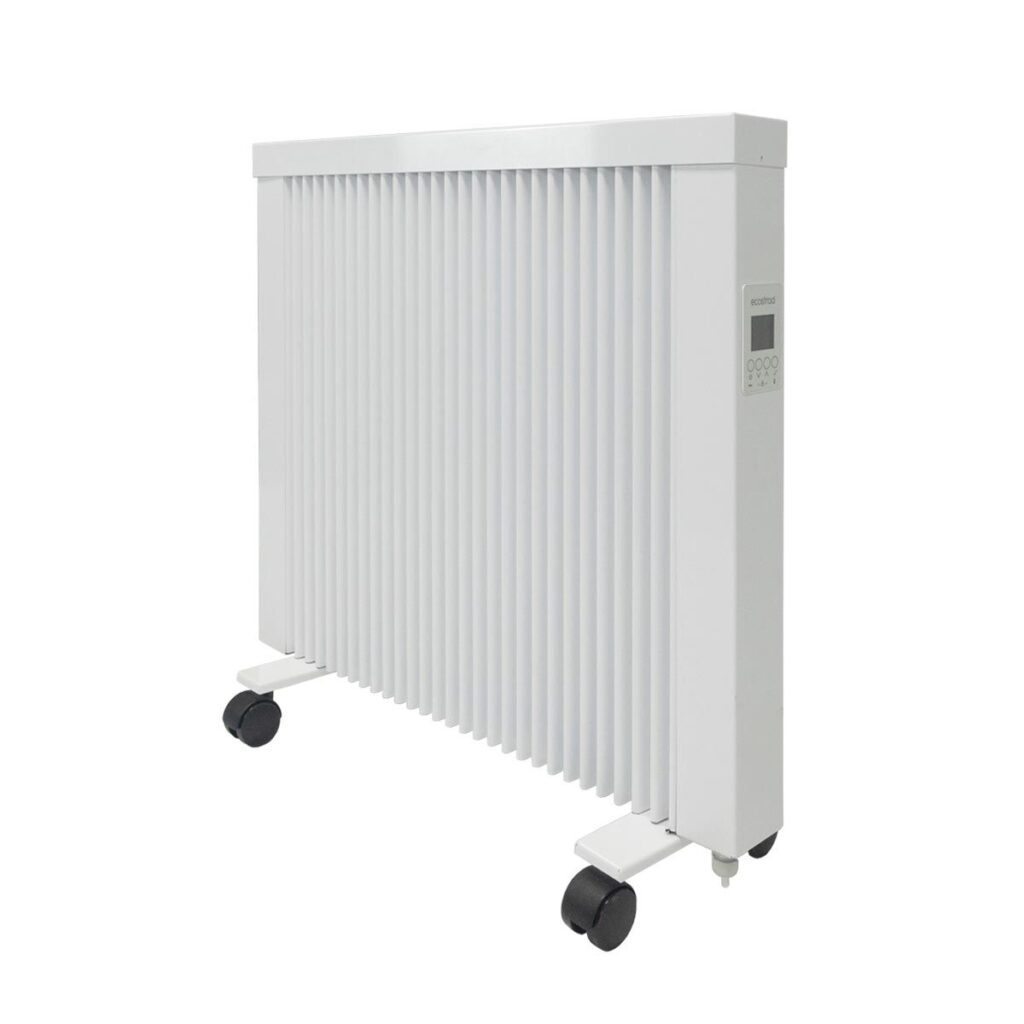

Ensuring Safety and Compliance: The Case of an Electric Radiator
Product Overview: An electric radiator is a common household appliance designed to provide heat. It functions by converting electrical energy into heat, which necessitates stringent safety measures to prevent electrical hazards.
Test Standards: For ensuring the safety and compliance of an electric radiator, the IEC 60335-1 standard is pivotal. This international standard, often harmonized under the EU’s Low Voltage Directive, sets out general safety requirements for household electrical appliances. It specifically includes provisions for electrical insulation resistance testing.
Importance of Compliance: Adhering to IEC 60335-1 is essential for electric radiators sold in the EU. Compliance with this standard implies conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental regulations. It’s a crucial step in obtaining the CE or UKCA marking, which is mandatory for selling such products in the European market.
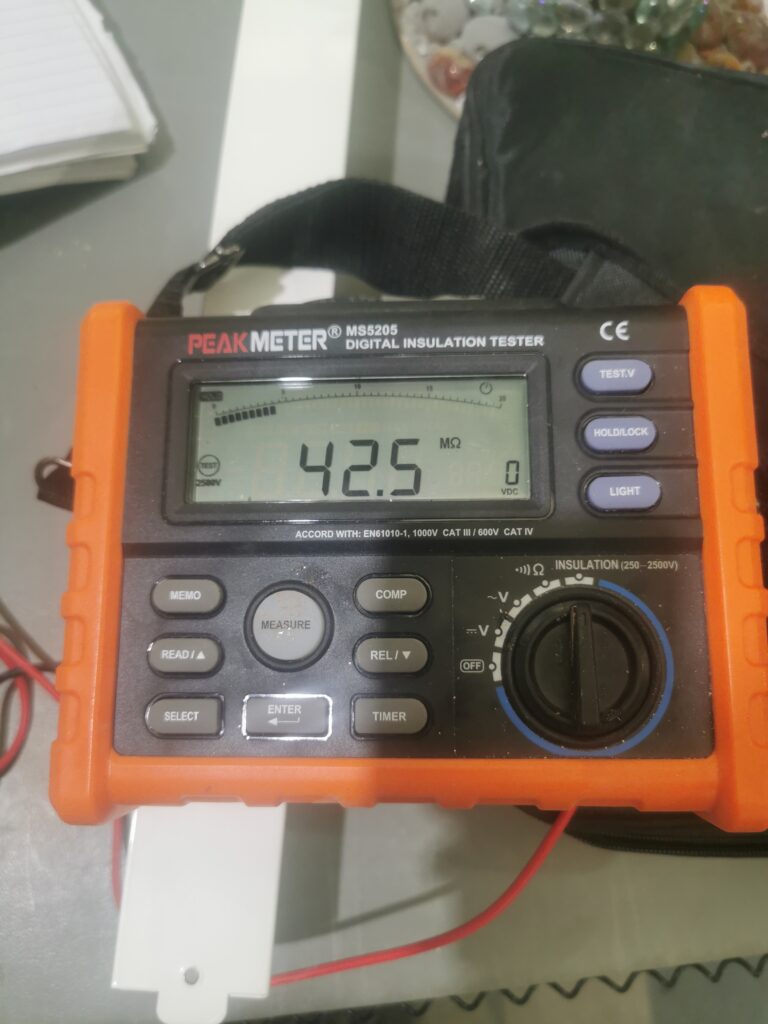
The Insulation Resistance Test: This test assesses the effectiveness of the electrical insulation in the radiator. It’s conducted using a high-voltage insulation resistance tester (megohmmeter). The test involves applying a high DC voltage between the radiator’s conductive parts and its casing and then measuring the resistance. This resistance indicates how well the insulation is preventing current flow, thereby ensuring safety against electric shocks and leaks.
Acceptable Outcome: A high resistance value, typically in megaohms (MΩ), is the desired result, indicating effective insulation. A low resistance reading would signify inadequate insulation, necessitating improvements for safety.
In summary, conducting an insulation resistance test in compliance with IEC 60335-1 is integral for ensuring the safety of electric radiators. It’s not just about regulatory compliance, but also about ensuring the product’s reliability and safety for end-users.
It is important to note that passing the insulation test as per BS EN 60335-1 (IEC) is a significant achievement but not sufficient on its own for the CE/UKCA mark. The BS EN 60335-1 standard includes a comprehensive array of test items, each vital to the product’s overall compliance. For full compliance and eligibility for the CE/UKCA marking, the electric radiator must successfully undergo and pass an extensive series of additional tests as required by these and other relevant regulatory standards. This comprehensive testing ensures that the appliance meets all necessary criteria for safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and, where applicable, energy efficiency.

To attain approval for the UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) mark for an electric radiator, it is essential to adhere to specific test standards that validate the product’s safety, quality, and performance. The primary standards include:
EN 60335-1: This standard is foundational for the safety of electrical appliances used in households and similar settings. It outlines general requirements applicable to all such appliances.
EN 60335-2-30: A subset of EN 60335, this standard specifically addresses the safety of room heaters, including detailed requirements for electric radiators.
EN 62233: This standard pertains to the methods for measuring electromagnetic fields of household appliances, focusing on human exposure considerations.
EN 55014-1 and EN 55014-2: These standards are crucial for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements. EN 55014-1 deals with emission standards, while EN 55014-2 focuses on immunity aspects, both applicable to household appliances, electric tools, and similar devices.
Additionally, electric radiators may need to comply with specific energy efficiency standards, depending on their design and operational mechanics. Lot 20 for example
Environmental Compliance: For many products, especially those sold in markets with strict environmental regulations, compliance with environmental standards is assessed. This might include testing for energy efficiency, emissions, and the use of hazardous substances.
Environmental compliance in product testing is increasingly vital, especially for markets with rigorous environmental regulations. This aspect of testing evaluates a product’s impact on the environment, encompassing energy efficiency, emissions, and hazardous substances.
Importance of Environmental Standards: Complying with environmental standards is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it aligns products with global sustainability goals and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products. Secondly, it helps manufacturers avoid legal penalties and market restrictions, as many regions now enforce strict environmental regulations. Thirdly, it plays a crucial role in reducing the overall ecological footprint of products, contributing to broader environmental protection efforts.
Example and Applicable Test Standards: Consider an LED light bulb, a product where energy efficiency and material safety are key. The relevant test standards would include:
- IEC 62560: Self-ballasted LED lamps for general lighting services. This standard assesses the energy efficiency and performance of LED lamps.
- RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) in the EU, which limits the use of specific hazardous materials in electronic products.
The LED bulb would be tested for its energy consumption against IEC 62560 criteria to ensure it meets energy efficiency benchmarks. Under the RoHS Directive, it would also be tested to confirm that it does not contain any of the restricted hazardous substances, like lead or mercury.
Acceptable Outcomes: For energy efficiency, the bulb should consume significantly less energy compared to traditional lighting solutions while providing adequate luminance. For hazardous substances, the bulb should be free from any materials exceeding the thresholds set by the RoHS Directive.
In summary, environmental compliance testing, exemplified here through the case of an LED light bulb, is integral to ensuring that products are sustainable and safe for the environment. Adhering to standards like IEC 62560 and the RoHS Directive not only satisfies regulatory requirements but also aligns products with the growing global demand for environmentally responsible solutions.
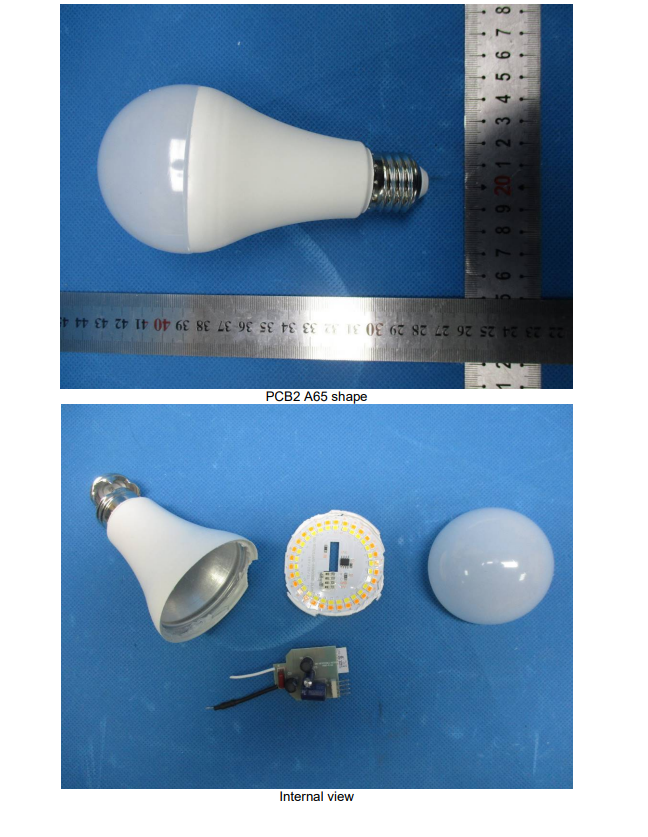
LED IEC 62650 Test
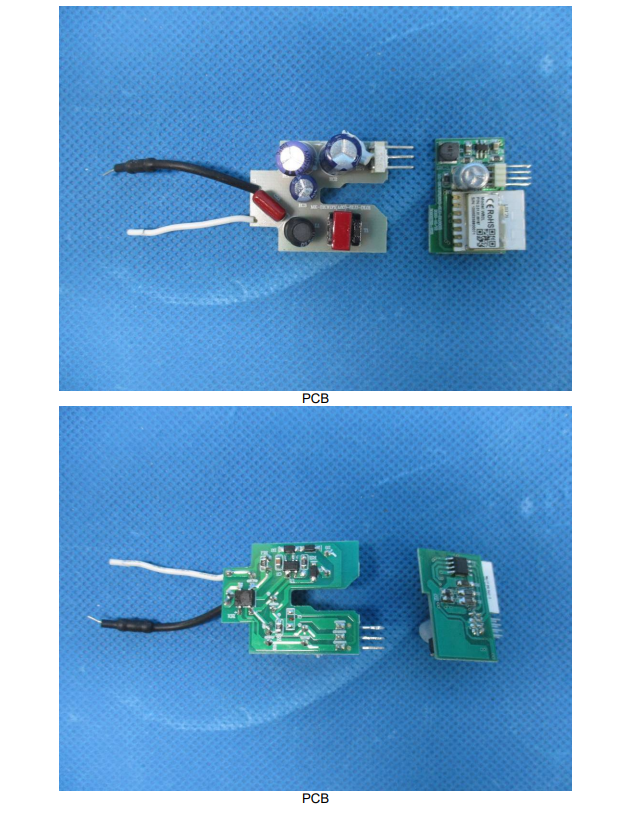

- Documentation and Reporting: After the testing is completed, the laboratory provides a detailed report outlining the tests conducted and the results. This report is essential for the next stages of certification. It serves as evidence of compliance and can be critical if the product’s compliance is ever questioned.
Foundation for Certification and Compliance The comprehensive documentation and reporting process that follows product testing are pivotal. Once testing is completed, the laboratory compiles a detailed report encompassing all tests conducted and their outcomes.
This documentation is not just a procedural requirement; it serves as the cornerstone for the next stages of product certification. It provides a clear, authoritative record of the product’s performance against the specified standards and regulations, essentially validating the product’s compliance.
This step is fundamental in transitioning from testing to officially certifying the product for market entry.
Evidence of Compliance and Accountability In the realm of product manufacturing and distribution, the test report serves a critical role as evidence of compliance.
This is particularly important in industries where safety and quality are highly regulated. Should any questions arise about the product’s compliance with safety, quality, or environmental standards, this report acts as a tangible proof point.
It demonstrates that due diligence was exercised in testing the product against recognized standards, which can be instrumental in addressing regulatory inquiries, customer concerns, or legal challenges.
Long-term Reference and Liability Mitigation Beyond immediate certification needs, the detailed test report is a valuable reference for the long-term lifecycle of the product.
In the event of issues or incidents in the future, such as customer complaints, safety recalls, or legal claims, this documentation becomes a crucial resource.
It provides a historical record of the product’s initial compliance and can help pinpoint whether issues arose from manufacturing inconsistencies, product modifications, or misuse. This can be vital for liability mitigation, helping to clarify responsibilities and potentially protecting the manufacturer from unwarranted claims.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is a field within electrical sciences focused on the unintended creation, transmission, and reception of electromagnetic energy, particularly concerning the undesirable impacts (known as Electromagnetic Interference, or EMI) that this energy can cause. EMC’s primary objective is to ensure that various devices utilizing electromagnetic phenomena can operate correctly within the same electromagnetic environment without causing or experiencing interference effects.

Enhancing Transparency and Consumer Trust Lastly, thorough documentation and reporting contribute significantly to transparency and consumer trust.
By maintaining detailed records of compliance and testing, manufacturers and distributors can demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety.
This transparency is increasingly valued by consumers and business partners alike, reinforcing brand integrity and consumer confidence in the product.
The process of documentation and reporting in product testing is a critical element, ensuring that products not only meet current standards but also providing a reliable record for future reference. This practice upholds accountability, fosters transparency, and is integral in building and maintaining trust in the product and the brand.
Feedback and Iteration: If the product fails to meet any of the standards, the manufacturer is provided with feedback on the areas of non-compliance. This allows them to make necessary modifications and improvements before retesting.
Re-testing if Necessary: In cases where the product fails to meet certain criteria, it may need to be re-engineered and retested. This iterative process continues until the product fully complies with all the applicable standards.
This comprehensive testing stage is vital in ensuring that the product is not only legally compliant but also safe, reliable, and of high quality. It’s a crucial step in protecting the manufacturer from legal issues and safeguarding the end-users from potential harm.
Stage 3: Detailed Documentation: The testing process must be thoroughly documented. This documentation includes detailed reports of the product specifications, testing procedures, methodologies, and the results of these tests. This step is crucial for providing proof of compliance and can be integral during audits or inspections.
Thorough Documentation of the Testing Process:
- This stage involves creating a comprehensive and detailed record of every aspect of the testing process.
- The purpose here is to ensure that every step, from the initial setup to the final result, is meticulously recorded.
- This documentation is not a mere formality but a vital part of the certification process, serving as a definitive record of the product’s compliance journey.
Elements of the Documentation:
- Product Specifications: This includes a complete and detailed description of the product, covering aspects like design, components, materials used, and intended functionality. It’s a blueprint that defines what the product is and what it’s supposed to do.
- Testing Procedures and Methodologies: Here, the focus is on how the tests were conducted. It involves detailing the specific methods and procedures followed, the standards adhered to, and the rationale behind choosing these methods. This section ensures transparency and replicability in the testing process.
- Results of the Tests: Perhaps the most critical part, this section records the outcomes of the tests. It’s not just about whether the product passed or failed but includes detailed data and observations that provide insight into the product’s performance under various conditions.
The Significance of Detailed Documentation:
- Proof of Compliance: This documentation acts as concrete evidence that the product has been tested and meets the required standards. It’s the hard proof that regulators, certification bodies, or clients might demand to verify compliance.
- Integral in Audits and Inspections: During audits or inspections, this documentation is indispensable. It provides auditors and inspectors with a clear trail of the testing process, allowing them to verify the product’s compliance independently.
- Facilitates Troubleshooting and Improvements: Should any issues arise with the product post-certification, this documentation helps in tracing back through the testing process to identify potential causes and facilitate improvements.
In essence, Detailed Documentation in product certification is not just a procedural requirement but a foundational aspect that underpins the integrity of the certification process. It serves multiple purposes, from being a testament to compliance, a guide in audits, to a tool for continual improvement. This comprehensive approach to documentation ensures that the product’s certification is reliable, verifiable, and sustainable over time.
Emphasizing the Importance of Certification Product certification is more than a regulatory hurdle; it’s a fundamental aspect of building trust and confidence in a product. In markets where consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny are high, certification can significantly influence product acceptance and success. It reassures customers and stakeholders about the product’s quality, safety, and reliability, which can be decisive factors in their purchasing decisions.
Ready to Ensure Your Product's Compliance with Confidence?
Section 2: Understanding Key Certification Marks
EAC Mark: Detailed Analysis and Requirements The Eurasian Conformity (EAC) mark is a critical certification symbol for products entering the markets of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) countries, including Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Kyrgyzstan. This mark signifies that a product complies with all the EAEU’s health, safety, and environmental protection standards. The process of obtaining an EAC mark involves a comprehensive assessment of the product’s adherence to these standards, which may include testing for toxicity, electrical safety, and environmental friendliness.
The presence of the EAC mark on products ensures consumers and authorities that these products meet the necessary regulatory requirements across the member countries. It encompasses a wide array of products, ranging from electronics and machinery to food items and textiles, thereby assuring a uniform standard of quality and safety. By displaying the EAC mark, manufacturers and suppliers demonstrate their commitment to adhering to the stringent standards of the EAEU, facilitating smoother market entry and consumer trust within these nations.

The Eurasian Conformity (EAC) mark is required for a broad range of products that are traded within the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) member states. Some specific categories of items that need to conform to this certification include:
Electrical Equipment and Appliances: This includes household electrical appliances, lighting equipment, and electronic devices. Products such as refrigerators, washing machines, televisions, and computers fall under this category.
Machinery and Industrial Equipment: Machinery used in manufacturing, construction, and agriculture, as well as related safety components, need EAC certification. This can range from industrial machinery, tractors, and elevators to boilers and safety equipment.
Medical Devices and Equipment: Medical products, including diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and various types of medical apparatus, require compliance to ensure safety and efficacy.
Vehicles and Automotive Parts: This encompasses cars, trucks, motorcycles, as well as automotive components such as tires, engines, and safety systems.
Toys and Children’s Products: Products intended for children, including toys, games, and childcare articles, must meet specific safety standards and carry the EAC mark.
Personal Protective Equipment: Items such as safety helmets, protective clothing, and respiratory protection devices fall under this category.
Food Products: Certain food items, including processed foods, beverages, and agricultural products, must comply with EAC standards to ensure they meet health and safety regulations.
Textiles and Clothing: Apparel, textiles, and related products are also subject to EAC certification to ensure they adhere to safety and quality standards.
Cosmetics and Hygiene Products: These include a wide range of personal care products, from soaps and shampoos to cosmetics and perfumes.
Each category of products has specific standards and regulations that must be met to obtain the EAC mark, ensuring that they are safe for use and comply with the necessary health and environmental protection standards.
What are the differences between the CE and the EAC mark?
The Eurasian Conformity (EAC) mark and the CE mark are both certification marks that indicate compliance with a set of standards and regulations, but they serve different economic regions and have distinct requirements.
EAC Mark:
- Geographic Scope: The EAC mark is applicable in the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), which includes Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Kyrgyzstan.
- Standards Covered: The EAC mark signifies compliance with the technical regulations of the EAEU. These regulations encompass a wide range of product categories, focusing on safety, health, and environmental protection.
- Regulatory Framework: The EAC mark is governed by the EAEU’s regulatory framework, which might have different standards and testing protocols compared to European standards.
CE Mark:
- Geographic Scope: The CE mark is used in the European Economic Area (EEA), which includes the EU member states along with Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
- Standards Covered: Products bearing the CE mark comply with European Union legislation, particularly regarding health, safety, and environmental protection.
- Regulatory Framework: The CE mark is governed by various EU directives and regulations, each relevant to specific product categories, such as the Low Voltage Directive, Machinery Directive, and so forth.
Key Differences:
- Geographical Validity: The most apparent difference is their geographic validity – the EAC mark is recognized in EAEU countries, while the CE mark is recognized in EEA countries.
- Underlying Standards and Directives: The standards and technical requirements underpinning these marks differ. The CE mark adheres to EU directives, which may have different requirements compared to EAEU technical regulations covered by the EAC mark.
- Certification Processes: The processes to obtain these marks can vary. For instance, the requirements for documentation, testing, and compliance verification might be different, reflecting the distinct legal and regulatory environments of the EAEU and EU.
- Market Accessibility: Products intended for sale in the EAEU require the EAC mark, while those for the EEA market need the CE mark. A product aiming for distribution in both markets must comply with both sets of standards and carry both marks.
While both the EAC and CE marks serve as indicators of compliance and allow market access, they are distinct in their geographic application, underlying standards, and the specific requirements needed to obtain them. Manufacturers aiming to sell products in both regions must ensure compliance with each set of standards and understand the specific requirements of each certification mark.
CE Mark: Understanding and Legal Implications The CE mark, short for “Conformité Européenne” (European Conformity), is a mandatory conformity marking for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). This mark indicates that a product meets all the EU’s safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. To achieve CE marking, products must undergo evaluation processes, which could include self-assessment, inspection by a notified body, or compliance with European technical standards.
Scope of the CE Mark:
- Mandatory Requirement: The CE mark, signifying “Conformité Européenne” (European Conformity), is a mandatory mark for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). Its presence on a product is a legal requirement, not optional.
- Indication of Compliance: Products bearing the CE mark are declared to comply with the EU’s safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This mark is a manufacturer’s declaration that the product meets all the necessary requirements of the relevant EU legislation.
- Wide Range of Products: The CE mark is applicable to a vast array of products, including electronics, medical devices, toys, machinery, and construction products.
Harmonized Standards for CE Marking play a critical role in the process of certifying products for the European market. These standards are essential in the CE marking process, providing specific technical guidelines and criteria that products must meet to be sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). Here’s a detailed explanation of what these standards are and how they are used in testing components for CE marking:
What are Harmonized Standards?
Definition and Purpose:
- Harmonized Standards are technical specifications (European Norms or ENs) developed by recognized European Standards Organizations: CEN, CENELEC, or ETSI.
- They provide detailed methods and criteria for ensuring that products comply with high-level safety, health, and environmental requirements set out in EU Directives or Regulations.
Legal Framework:
- These standards are harmonized under EU legislation, meaning they are recognized across all member states.
- Compliance with a harmonized standard provides a ‘presumption of conformity’ with the corresponding requirements of the relevant EU Directive or Regulation.
How Harmonized Standards are Used in CE Marking Process:
Identification of Relevant Standards:
- Manufacturers must first identify which harmonized standards are relevant to their product. Different products, like electronics, toys, or machinery, have different applicable standards.
Testing and Assessment:
- Self-Assessment: For many products, manufacturers can conduct internal testing and assessment to ensure the product meets the specific criteria outlined in the applicable harmonized standard(s).
- Third-Party Assessment: Some products, particularly those in higher-risk categories, may require testing and certification by an external ‘Notified Body’. This is an organization designated by an EU country to assess the conformity of certain products before being placed on the market.
Technical Documentation:
- Manufacturers must compile technical documentation demonstrating that the product meets the requirements of the harmonized standards. This documentation includes test reports, technical details about the design, manufacture, and operation of the product, and a risk assessment.
Declaration of Conformity:
- Once a product is found to comply with all relevant harmonized standards, the manufacturer issues a Declaration of Conformity (DoC). This is a statement declaring that the product meets all applicable EU requirements.
Affixing the CE Mark:
- After issuing the DoC, the manufacturer can then affix the CE mark to their product, indicating it complies with the necessary EU regulatory requirements.
Importance in Component Testing:
- Component-Level Compliance: In many cases, not only the final product but also individual components must meet the requirements of relevant harmonized standards. This is especially critical in electronic and mechanical products where the safety and functionality of the entire system depend on the reliability of its components.
- Ensuring Overall Product Compliance: By ensuring each component complies with harmonized standards, manufacturers can more confidently assert that the final product also complies with the necessary EU directives and regulations.
Harmonized standards are integral to the CE marking process, providing a clear and consistent framework for manufacturers to ensure their products meet EU requirements. By following these standards, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to safety, quality, and compliance, facilitating the free movement of their products within the EEA.
Selecting the correct harmonized standards for a product to comply with CE marking requirements involves several key steps. It’s a process that requires thorough understanding of the product, its applications, and the relevant EU directives. Here’s a detailed guide on how someone would select the appropriate harmonized standards:
Understanding the Product and its Application
Product Analysis:
- Identify the product’s nature, purpose, and functionalities. This includes understanding its design, material composition, and intended use.
- Assess the potential risks associated with the product. Consider how it will be used and what safety or health risks it might pose.
EU Directives and Regulations:
- Identify which EU Directives or Regulations apply to your product. The CE marking applies to a wide range of products, from toys to medical devices, and each category has specific directives. For instance, electronic equipment falls under the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive, machinery under the Machinery Directive, etc.
Researching Harmonized Standards
Finding Relevant Standards:
- Use the Official Journal of the European Union (OJEU) as a starting point. It publishes references to harmonized standards that provide presumption of conformity to specific directives.
- Search databases like EUR-Lex, which provide access to EU law, including directives and harmonized standards.
Comparing Product Specifications with Standard Requirements:
- Go through the details of the identified harmonized standards. Compare the criteria and testing methods in the standards with your product specifications.
- Ensure that the standards cover all relevant aspects of your product – safety, health, environmental concerns, etc.
Consulting Experts and Notified Bodies
Seek Expert Advice:
- If the selection process is complex or if you are uncertain, it’s advisable to consult with experts in CE compliance or standards.
- They can provide insight into which standards are most relevant to your product and guide you through the compliance process.
Engagement with Notified Bodies:
- In cases where third-party assessment is required (for higher-risk products), contact a Notified Body. They can perform conformity assessments and validate that the correct standards are being applied.
- Notified Bodies have the expertise to interpret the standards and directives accurately, ensuring that your product undergoes the appropriate evaluations.
Staying Updated
- Monitor Changes: Harmonized standards are periodically updated to reflect new safety research, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Stay informed about any updates or new standards that might affect your product.
Documentation and Record Keeping
- Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of how you determined which harmonized standards apply to your product. Document your research, expert consultations, and any correspondence with Notified Bodies.
In summary, selecting the correct harmonized standards is a meticulous process that requires a deep understanding of your product, relevant EU directives, and the specific standards themselves. It often benefits from expert input and should be approached with thorough research and careful documentation to ensure compliance and facilitate smooth market entry in the European Economic Area.
Examples of Harmonized Standards for CE Marking:
Low Voltage Directive (LVD) – EN 60335-1:
- Applies To: Electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits.
- Focus: Ensures electrical safety in consumer appliances and other electrical equipment.
- Standard Example: EN 60335-1, which covers the safety of household and similar electrical appliances.
Machinery Directive:
- Applies To: Machinery and certain parts of machinery.
- Focus: Addresses issues like mechanical safety, risk of injury, and ergonomic requirements.
- Standard Example: EN ISO 12100, providing basic concepts, principles for design, and general aspects of safety.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive:
- Applies To: Equipment liable to cause electromagnetic disturbance or the performance of which is liable to be affected by such disturbance.
- Focus: Ensures that electrical and electronic equipment does not generate, or is not affected by, electromagnetic disturbance.
- Standard Example: EN 55032 for multimedia equipment – Emission requirements.
Construction Products Regulation (CPR):
- Applies To: All construction products.
- Focus: Ensures that products are fit for their intended use, particularly in relation to health and safety.
- Standard Example: EN 13162, which covers thermal insulation products for buildings.
RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances):
- Applies To: Electrical and electronic equipment.
- Focus: Restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
- Standard Example: EN 50581, providing technical documentation requirements for demonstrating conformity.
Toy Safety Directive:
- Applies To: Toys.
- Focus: Addresses safety aspects like flammability, chemical properties, and mechanical properties.
- Standard Example: EN 71 series, which includes safety requirements for toys.
The CE mark serves as a passport for products to enter the European market, ensuring they adhere to the highest standards of safety, health, and environmental protection. The standards covered under the CE marking framework are designed to be harmonized across all EU member states, providing a unified criterion for product evaluation. Compliance with these standards is a testament to the product’s quality and adherence to European regulatory expectations.
UKCA Marking
The UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) mark, similar to the CE mark, is a regulatory mark that signifies a product’s compliance with UK standards and regulations. Since the UK’s exit from the European Union, the UKCA mark has become increasingly significant.

Selection of Harmonized Standards for UKCA Marking:
Understanding the Product and its Application:
- Like the CE mark, the first step in UKCA compliance is a thorough understanding of the product, including its design, intended use, and potential risks.
- Determine which UK-specific regulations and standards apply. While many UK standards initially mirrored EU standards, there may be divergences, especially in future updates.
Researching Relevant Standards:
- For UKCA marking, manufacturers should refer to UK-specific guidance and publications that list the relevant standards. These are often parallel to the EU’s harmonized standards but are specific to the UK regulatory environment.
- The UK Government’s website and UK-specific standard organizations are primary resources for finding these standards.
Consulting Experts and UK Approved Bodies:
- In the UK, ‘Approved Bodies’ (previously known as Notified Bodies in the EU context) play a role in assessing and validating compliance with UKCA standards for certain products.
- Consulting with UK-specific regulatory experts can aid in understanding the nuances of UKCA compliance.
The UKCA Mark: Current State and Differences from the CE Mark
Legal Implications:
- The UKCA mark is mandatory for products sold in Great Britain (England, Wales, and Scotland). It covers most goods that previously required the CE mark.
- Unlike the CE mark, which is recognized across the European Economic Area, the UKCA mark is only valid within the UK.
Future of UKCA Mark:
- As UK-specific regulations and standards evolve post-Brexit, it’s expected that UKCA requirements may diverge more significantly from CE standards.
- Manufacturers should stay vigilant about ongoing regulatory changes to ensure continued compliance.
Transition Period:
- Currently, there’s a transition period where products with the CE mark are still accepted in the UK market, allowing manufacturers time to adjust. However, this period is temporary, and full compliance with the UKCA mark will eventually be required.
Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Documentation for UKCA compliance follows a similar detailed process, including product specifications, testing methodologies, and test results.
- The primary difference lies in ensuring that the standards and regulatory references are specific to the UK.
Anticipating Changes in UKCA Standards
- The UK may develop its own standards and testing procedures in the future, potentially leading to differences from the current EU-aligned standards.
- It’s crucial for manufacturers to monitor these developments to adapt to new UK-specific requirements.
The UKCA mark represents the UK’s commitment to maintaining product safety and quality post-Brexit. While it currently shares many similarities with the CE mark, the potential for divergence in standards and regulations is significant. Manufacturers should prepare for these changes and keep abreast of the evolving UK regulatory landscape to ensure ongoing compliance. The UKCA mark not only signifies conformity to current standards but also symbolizes a new era of UK-centric product certification and regulation.
Other Global Certification Marks
FCC (Federal Communications Commission) – USA: This mark is critical for electronic products in the USA, ensuring they do not cause harmful electromagnetic interference. The FCC certification process focuses on testing the electronic emissions of products and their impact on the environment and public health.


UL (Underwriters Laboratories) – Global: A global safety certification, UL covers a broad range of products, focusing on safety standards for electrical devices and components. UL certification means a product has been tested to high safety standards and is deemed safe for public UL certification ensures that a product has been tested to high safety standards and is deemed safe for public use. This process typically involves rigorous testing of electrical devices and components to evaluate their safety, durability, and performance under various conditions. Obtaining UL certification is a testament to a product’s quality and reliability, making it a respected mark of safety across numerous industries.
CSA (Canadian Standards Association) – Canada: Similar to UL, the CSA mark signifies compliance with Canadian safety standards. It encompasses a wide range of products, focusing primarily on electrical and mechanical devices. The CSA certification process includes thorough testing and inspection to ensure that products meet the high safety and performance standards required in Canada.

Section 3: Compliance and Legal Responsibilities
The Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with product certification requirements can have far-reaching consequences. Financial penalties can be substantial, particularly if non-compliance leads to safety issues or consumer harm. For instance, companies might face fines amounting to a significant percentage of their annual revenue, depending on the severity of the infringement and the legislation of the particular country or economic area. Legal action, including lawsuits, can arise, especially if a product causes harm or injury. This could involve class-action lawsuits in cases where multiple consumers are affected, leading to both financial and reputational damage.
While our approach in presenting information may sometimes include light-hearted imagery, it’s crucial to emphasize that non-compliance with CE marks and certification standards is a serious matter. Certification, especially CE marking, is not just about adhering to regulatory requirements; it’s fundamentally about ensuring the safety and well-being of users. Failure to comply can lead to significant harm to individuals, whether through product malfunction, safety hazards, or health risks. Moreover, non-compliance can have severe consequences for manufacturers, including legal repercussions, financial penalties, and irreparable damage to the brand’s reputation. Therefore, maintaining strict adherence to certification standards is not only a legal obligation but a moral imperative to protect consumers and uphold public safety.

In addition to legal repercussions, non-compliant products may be withdrawn from the market, leading to lost sales and a damaged brand reputation. A recall process not only incurs direct costs but also indirectly affects customer trust and loyalty. Moreover, failure to comply with certification standards can prevent products from entering certain markets, severely limiting a company’s market reach and growth potential. This can be particularly damaging in industries where global distribution is key to business success.
Furthermore, non-compliance can lead to a cascade of negative impacts, including strained relationships with business partners and distributors, increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, and potential barriers in future market entries. For instance, a technology company failing to meet electronic safety standards might find its products barred from major markets, leading to a significant loss in potential revenue and long-term strategic setbacks.
In some sectors, non-compliance can have even more severe consequences, such as in the pharmaceutical or medical device industries, where patient safety is paramount. Here, non-compliance can lead to severe health risks for consumers, resulting in not just financial and legal consequences but also ethical implications.
In summary, the consequences of non-compliance extend well beyond immediate financial penalties, encompassing legal, reputational, operational, and strategic aspects of a business.
Legal Responsibilities of Manufacturers and Importers
Manufacturers and importers have the primary responsibility for ensuring that their products meet the necessary certification standards. This responsibility is not only a legal requirement but also a moral and ethical one, especially in industries where product safety is critical. Understanding relevant standards applicable to their products and target markets is the first step in this complex task. For example, a manufacturer of children’s toys must be intimately familiar with safety standards related to toxicity, choking hazards, and durability.
Ensuring product compliance involves conducting or arranging necessary testing. This could include, for instance, sending samples to accredited testing laboratories or implementing in-house testing processes for ongoing quality assurance. Moreover, every aspect of the product must comply with the relevant standards, from design and manufacturing to packaging and labeling.
Maintaining detailed records of testing, compliance, and certification is crucial for audit purposes and proving compliance during inspections. This documentation can be extensive, including test reports, certification documents, technical files, and risk assessments. For instance, a company producing electrical appliances might need to maintain detailed records of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) tests and conformity assessments to specific standards like the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) in the EU.
Continuous monitoring and adaptation to changing standards and regulations are essential to maintain compliance over time. This is especially pertinent in rapidly evolving sectors such as technology or pharmaceuticals, where regulations can change in response to new discoveries or emerging safety concerns. Companies must therefore invest in ongoing training for their compliance teams and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Navigating Through the Legal Landscape of Product Certification
The legal landscape of product certification is complex and varied, requiring manufacturers and importers to stay informed about changes in regulations and standards. This task is particularly challenging in a global market where each country or region may have its own set of regulations. For example, a manufacturer selling products in both the EU and the US must navigate the CE marking requirements in the EU and the FCC regulations in the US.
Seeking expert advice from legal experts or compliance specialists is crucial in navigating this landscape effectively. These experts can provide insights into not only current regulations but also emerging trends and potential future changes. They can also assist in interpreting the often technical and complex language of regulatory standards.
Building compliance considerations into product design and development can help prevent issues later in the certification process. For instance, integrating safety features into the initial design of a product can be more cost-effective than making modifications after a product fails to meet certification standards.
Proactive risk management, including identifying and managing potential compliance risks early, can save significant time and resources. This might involve conducting preliminary risk assessments during the product development phase or engaging with regulatory bodies for pre-market consultations.
Navigating the legal landscape of product certification requires a proactive, informed, and systematic approach. It involves not just compliance with existing standards but also anticipation of future changes and integration of compliance into every stage of the product lifecycle.
The consequences of non-compliance with product certification requirements can be severe and multifaceted. Financially, non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties. For instance, in 2019, the average fine for non-compliance was a staggering 145.33 million US dollars, with some fines reaching as high as 1 million dollars or more. Legally, non-compliance can result in litigation, fines, imprisonment, and even license revocation, depending on the severity of the violation. This is particularly crucial in industries like healthcare, where patient safety is directly impacted.
Reputationally, non-compliance can lead to a significant loss of trust among customers, investors, and other stakeholders. Notable companies that have suffered reputational damage due to non-compliance issues include Danske Bank, 1MDB, Odebrecht, Petrobras, and Siemens. The impact on a company’s public image can lead to declines in sales, drops in stock prices, and a tarnished brand image.
In essence, non-compliance not only incurs financial and legal penalties but also severely damages a company’s reputation, affecting its long-term viability and success. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to prioritize compliance efforts, stay informed about the laws and regulations governing their operations, and implement robust compliance programs. This helps not only in avoiding penalties but also in fostering a culture of integrity and responsibility within the organization
Section 4: Industry-Specific Certification Requirements
Electronics and Electrical Appliances This sector is governed by stringent certification requirements due to the inherent risks associated with electrical devices. Key aspects of certification include adhering to safety standards, ensuring energy efficiency, compliance with EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) requirements, and adhering to directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment).
Toys and Children’s Products Given the vulnerability of their end-users, children’s products and toys undergo rigorous testing and certification processes. These processes ensure they are safe, free from harmful materials, and appropriate for various age groups. Critical components of certification include safety testing for physical and mechanical properties, chemical compliance (such as testing for lead and phthalates), and age grading to ensure the toy is suitable for the intended age group.
Medical Devices and Healthcare Products The medical device and healthcare industry is one of the most heavily regulated sectors. Products in this category require certifications like FDA approval in the United States and CE marking in Europe. Compliance with ISO standards, particularly ISO 13485 (Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes), is critical to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of medical products.
Food and Beverage Industry In the food and beverage industry, certifications are required to ensure products are safe for consumption. These include HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) certification, which focuses on identifying and preventing hazards that could cause foodborne illnesses. FDA regulations in the U.S. and various EU directives govern food safety standards. Additionally, certifications like organic and GMO-Free are important for certain market segments focused on natural and non-genetically modified products.
Automotive Industry The automotive industry faces stringent regulations to ensure vehicle safety, environmental compliance, and overall quality. Safety standards are paramount, and certifications may include crash test ratings and emissions testing. Environmental regulations focus on reducing the environmental impact of vehicles, including emissions standards like Euro 6 in Europe. Quality management certifications, such as ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949), are essential for demonstrating a commitment to quality and continuous improvement in automotive manufacturing.
Textiles and Apparel This industry deals with certifications concerning material safety, sustainability, and ethical labor practices. Material safety certifications like OEKO-TEX ensure that textiles are free from harmful substances. Sustainability certifications like the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) focus on the entire supply chain of textile products, from raw materials to finished goods, ensuring environmentally and socially responsible manufacturing. Compliance with fair labor standards is also crucial to ensure that products are produced under ethical working conditions.
Navigating the complex landscape of product certification, especially understanding and complying with the intricate requirements of the EAC, UKCA and CE marks, is a challenging task that can significantly impact market access and consumer trust. Whether it’s ensuring electrical appliances meet safety standards, verifying the compliance of medical devices, or confirming the environmental friendliness of consumer goods, each product category demands thorough attention to detail and expertise in regulatory frameworks.
This is where our services come into play. We specialize in guiding businesses through the intricate process of obtaining certification marks like the EAC and CE, ensuring that your products not only meet the rigorous standards of health, safety, and environmental protection, but also gain smooth market entry and enhanced consumer confidence. Don’t navigate this complex process alone; let our expert team help you achieve compliance and expand your market presence with confidence. Contact us today to ensure your products meet all necessary certification requirements and are ready for success in the global market.

